
Benefits
 Research show that drinking water contains over 2000 harmful chemicals and EPA regulations only set standards for about 50 of them...
Research show that drinking water contains over 2000 harmful chemicals and EPA regulations only set standards for about 50 of them...About Water
Kuwait is a hyper-arid state without rivers or fresh-water aquifers. Nonconventional water resources, including brackish groundwater, seawater desalination, and reclamation of treated waste water are the main current sources of water supply, of which the quality is as saline as 1,000-45,000 mg of total dissolved solids (TDS) per litre:
The availability of well water in Kuwait is very limited and even the finest sources requires further purification to reduce TDS. The table below shows the details of wellfields in Kuwait.
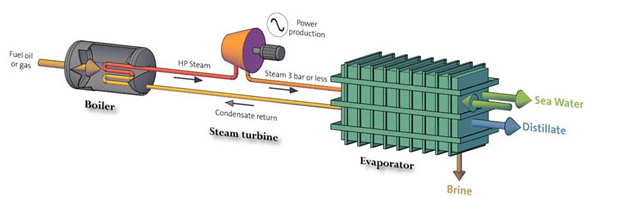
Schematic of a Co-generation desalination plant
A variety of chemicals being introduced during thermal desalination process. Mostly these are intended for the safeguarding of plant machinery and pipe lines. Table below profiles chemicals which are most frequently used in seawater thermal desalination.
Dose rates are only indicative and are shown as mg/litre of chemical in the relevant process stream (MU=Make Up Water, CW=Cooling Water).
Table 2.1 Chemicals used in thermal desalination processes
Chlorination
Chlorine, the most common disinfectant, is effective in killing most pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The output water from desalination plants is chlorinated at local distribution centres to provide a residual concentration of 0.5 to 2.0 ppm. Chlorine is not effective in killing certain protozoans like cryptosporidium, however.
One complication that arises with chlorination is the formation of by-products during the disinfection process. Chlorination by-products are chemicals that result from the reaction of chlorine with organic substances in water. Table below lists some common chlorination by-products.
Concentrations found in chlorinated waters
Disinfection by-products have been linked to adverse health effects, including cancer, in laboratory animals. Table 2 summarizes the health effects of some chlorination by-products.
groundwater (shallow), 1,000-2,000 mg/l,
brackish groundwater, 2,000-8,000 mg/l,
seawater, 45,000 mall,
product water from MSF (multi-stage flash) desalination, 25-50 mg/l,
reclaimed treated waste water, 2,500 mg/l.
Well water
The availability of well water in Kuwait is very limited and even the finest sources requires further purification to reduce TDS. The table below shows the details of wellfields in Kuwait.
| Field
|
Aquifer
|
No. of wells | Yield(million m³/year)
|
Salinity (TDS, mg/l)
|
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Existing | Potential
|
||||
| Rawdatain and Um al-Aish |
Dibdibba F | 52
|
2.5
|
6.6
|
700-1,200
|
| Shigaya A, B. C
|
|
60
|
53
|
66 | 3,000-4,000 |
| Shigaya D, E
|
DammanF
|
54
|
-
|
42 | 3,000-4,500
|
| Sulaibiya
|
Damman F
|
133 | 25-33
|
33
|
4,500-5,500 |
| Abduliya
|
Damman F
|
14
|
8
|
-
|
4,500
|
| Wafra
|
|
(110)
|
33-42
|
50
|
4,000-6,000
|
| Abdali-Um Nigga
|
Dibdibba F
|
(110)
|
20-25
|
33-42 | 3,000-7,000
|
Source: Kuwait Institute for Scientific Research, in 1990. |
|||||
Municipal Tap Water
Kuwait is one of the world's leaders in the production of fresh water from the sea. Large Multi Stage Flash (MSF) distillation plants are often paired with power plants in a Co-generation configuration. Waste heat from the power plant is used to heat the seawater, providing cooling for the power plant at the same time. Kuwait developed Co-generation stations, in the early 1950s and have been in use since then. The annual production of fresh (distilled) water is estimated to be now 366 million m³.
Installed capacity of co-generation stations in Kuwait
Kuwait is one of the world's leaders in the production of fresh water from the sea. Large Multi Stage Flash (MSF) distillation plants are often paired with power plants in a Co-generation configuration. Waste heat from the power plant is used to heat the seawater, providing cooling for the power plant at the same time. Kuwait developed Co-generation stations, in the early 1950s and have been in use since then. The annual production of fresh (distilled) water is estimated to be now 366 million m³.
Installed capacity of co-generation stations in Kuwait
| Fresh water production | Power generation (MW) | Date | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Million m³/year Mig/day | ||||
| Shuwaikh | 53 | 32 | 324 | 1960-70 |
| Shuaiba North |
|
14
|
400 | 1965-71 |
| Shuaiba South | 50 | 30
|
804 | 1971-75 |
| Doha East
|
71 | 43 | 1,158 | 1978-79 |
| Doha West | 159
|
96 | 2,400 | 1985
|
| Az-Zour South |
|
|||
| stage I | 10
|
06 | ||
| stage II | 119 | 72 | 2,511 | 1991 |
| Total | 366 | 221 | 5,769 | |
Source: Kuwait Institute for Scientific Research, in 1990. |
||||
Schematic of a Co-generation desalination plant

A variety of chemicals being introduced during thermal desalination process. Mostly these are intended for the safeguarding of plant machinery and pipe lines. Table below profiles chemicals which are most frequently used in seawater thermal desalination.
Dose rates are only indicative and are shown as mg/litre of chemical in the relevant process stream (MU=Make Up Water, CW=Cooling Water).
Table 2.1 Chemicals used in thermal desalination processes
| Chemical Type | Purpose of Use | Dose And Feed Location |
Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scale inhibitor (Usually phosphonates, polyphosphate, polymaleic or polycarboxylic acids, or a blend of several of these) | Usually crystal modifiers that avoid precipitation and development of deposits (primarily CaCO3, Mg (OH)2. Blends may include dispersant properties to prevent crystals adhering to equipment. | 1-8 mg/litre, MU | Used in all thermal desalination processes. |
| Acid (usually sulphuric acid), | An alternative scale inhibitor. By lowering pH calcium carbonate and magnesium hydroxide scale formation is avoided. |
≈100 mg/litre, MU | Used only in MSF desalination. |
| Antifoam (Poly Othelyne Ethylene Oxide or similar surfactant) | Uncorrected foaming due to unusual feed water conditions may overwhelm the process indicated by high product TDS (carryover). | ≈0.1 mg/litre, MU | Used intermittently in all thermal processes but primarily MSF. |
| Oxidizing Agent: most | To control bio-fouling and | ≈1.0 mg/litre, | Used for large surface and sea |
| often a form of chlorine, | aquatic organism growth in | CW | water intakes. |
| however biocides may | the intake and desalination | ||
| have some use, particularly | equipment. Continuous | ||
| for smaller systems. | dosing of 0.5-2 mg/L active Cl2 with intermittent shock dosing (site specific but may be 3.7 mg/L for 30-120 minutes every 1-5 days). | ||
| Sodium bisulfite. | Oxygen scavenger to remove traces of residual oxygen or chlorine in the brine recirculation. |
≈0.5 mg/litre, MU |
Used only in MSF desalination systems and in intermittent mode. |
Chlorination
Chlorine, the most common disinfectant, is effective in killing most pathogenic bacteria and viruses. The output water from desalination plants is chlorinated at local distribution centres to provide a residual concentration of 0.5 to 2.0 ppm. Chlorine is not effective in killing certain protozoans like cryptosporidium, however.
One complication that arises with chlorination is the formation of by-products during the disinfection process. Chlorination by-products are chemicals that result from the reaction of chlorine with organic substances in water. Table below lists some common chlorination by-products.
Concentrations found in chlorinated waters
| Chloroform | Range 0.7 - 540 µg/L, Mean 26.4 µg/L |
| Bromodichloromethane | Range 1.9 - 183 µg/L, Mean 9.1 µg/L |
| Chlorodibromomethane | Range 0.4 - 280 µg/L, Mean 5.7 µg/L |
| Bromoform | Range 0.4 - 280 µg/L, Mean 5.7 µg/L |
| Chloroacetic Acid | Range <1 - 5 µg/L |
| Dichloroacetic Acid | Range 12 - 79 µg/L, Mean 47 µg/L |
| Trichloroacetic Acid | Range 4 - 103 µg/L, Mean 38 µg/L |
| Dichloroacetonitrile | Range 1.9 - 24 µg/L, Mean 2 µg/L |
Disinfection by-products have been linked to adverse health effects, including cancer, in laboratory animals. Table 2 summarizes the health effects of some chlorination by-products.
| Health effects | |
|---|---|
| Chloroform | Animal carcinogen that can induce liver tumors in mice and kidney tumors in rats. |
| Bromodichloromethane | Produces liver and kidney damage in both mice and rats. Carcinogenic in mice and rats, producing renal, liver, and intestinal tumors. |
| Chlorodibromomethane | Produces liver and kidney damage in both mice and rats. Induces tumors in the liver of mice. |
| Bromoform | Low incidence of intestinal tumors in rats. |
| Chloroacetic Acid | Neurologic effects in animals. No increased tumors. |
| Dichloroacetic Acid | Major toxicities are damage to the nervous system and liver. Induces liver tumors in mice. |
| Trichloroacetic Acid | Potent inducer of liver tumors in male mice. |
| Dichloroacetonitrile | No specific toxicological effects reported, only nonspecific effects on body weight and some organ weights and some reproductive effects. |
Long-term risks of consuming chlorinated water include excessive free radical formation, which accelerates aging,
increases vulnerability to genetic mutation and cancer development, hinders cholesterol metabolism,
and promotes hardening of arteries.
Effect of boiling municipal water:
The recommend time bringing water to a boil for necessary disinfection, varies from 1-25 minutes. Boiling tap water for such prolonged period simply contributes to increased TDS. In reality, due to chlorination, the water is already disinfected. Boiling does not help to eliminate chlorination by-products or chemicals introduced during desalination process.
The recommend time bringing water to a boil for necessary disinfection, varies from 1-25 minutes. Boiling tap water for such prolonged period simply contributes to increased TDS. In reality, due to chlorination, the water is already disinfected. Boiling does not help to eliminate chlorination by-products or chemicals introduced during desalination process.

